Autonomous drone project
Since the late 1990s, the so-called micro air vehicle(MAVs) have attracted substantial and growing interests in the engineering and science community. The MAV was originally defined as a vehicle with a maximal dimension of 15 cm or less, which is comparable to the size of small birds, or bats, and a flight speed of 10-20 m/s . Equipped with a video camera of a sensor, these vehicles can perform surveillance and reconnaissance, targeting, and biochemical sensing at remote or other dangerous locations.
There is a great potential for interdiscpline research between biologists and engineers because micro air vehicle and biological flyer share similar dimensions. In addition, biological flyer posses neuron-based control capability that far exceed the current state of the state of art electronics-based control specifically in terms of power efficiency.
Prof Yang's group is currently engineering Do-it-yourself micro air vehicle or drone to enable neuromorphic chip guided flight of drone.
In particular, we are interested in using ~100 neuron scale to control mobile robot such as drone
極致的飛行機器 (ultimate mobile flight vehicle)– 微型無人機 (micro Drone)
自 1990 年代後期以來,所謂的微型飛行器 (Micro Aero Vehicle) 在工程和科學界引起了越來越大的興趣。 MAV 最初被定義為最大尺寸為 15 cm或更小的飛行器,可與小鳥或蝙蝠的大小相媲美,飛行速度為 10-20 m/s (McMichale and Francis, 1997)。因為 MAV 和生物飛行器具有相似的尺寸。此外,生物飛行器具有基於神經元的控制能力,特別是在電源效率方面,遠遠超過了當前基於電子技術的最先進控制能力。昆蟲大腦特別適用於資源受限的場景,例如飛行器,同時顯示出驚人的功能,使它們能夠輕鬆執行複雜的任務,例如(視覺)避免碰撞、定位、通信、導航、氣味源定位和未知不可預測環境中的社交互動
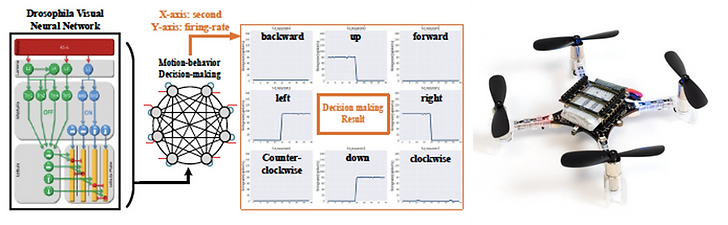
我們提出的整合晶片微型無人機(四軸飛行器),重量在 100 g 左右,因此在整個系統的功耗和電子系統都必需用新的運算晶片。這樣的重量產生的飛行的動能很低,安全行高,並且可以在窄小的空間進行監視的任務。於四軸飛行器上植入全域光流運動狀態偵測以及障礙物偵測神經網路,並以數位式突波神經晶片來降低功耗, 並執行晶片觸發的運動控制(motion control)。
Swimming bio-mimetic robots
Bio-inspired and bio-mimetic research have both grown steadily over the last few decades and allowed the development of modern, more life-like robots inspired by natural objects. Despite those more sophisticated designs, robots still fall short of the universality and robustness of animal movement and lag behind in important areas such as modulatiry. In our lab, we are working toward a modular swimming robot consisting of multiple body segment. The locomotion control is enabled by central pattern generator. The central pattern generator is a neural network that consists of non-linear neuron oscillator and generates rhythmic oscillator for servo motor control. Such a platform features low power (< 10 Watt) both in mechanical and computation domain and small body weight (< 1 kg) is very suitable for a wide variety of artificial intelligence and biomimetic experimentation.
With the support of NTHU’s innovation fund, my research group has also begun to develop multi-mechanical degrees of freedom fish robots, aiming to develop low-power, modular swimming robots that use the Kuramoto neural network model. The main research was published in the domestic conference such as Automation 2024 and the 29th Artificial Intelligence and Application Symposium (TAAI 2024). Derived research includes the walking robot of myriapod, published in IEEE CBS Nagoya 2024, as well as the crawling robot (Q robot) that uses the Q learning method (Q learning) in reinforcement learning, were published in TAAI and the Q robot also won the Runner-up paper award of TAAI 2024.
過去 20 年來,仿生和仿生研究都在穩步發展,並在生物的啟發下開發了更逼真的現代機器人。儘管有這些更複雜的設計,機器人仍然達不到動物運動的普遍性和穩健性,並且在模組化等重要領域中落後。我們的研究小組正在製作一個由多個身體部位組成的模組化游泳機器人。運動控制由中央模式產生器啟用。中央模式發生器是一個神經網路,由非線性神經元振盪器組成,並產生用於伺服馬達控制的節律振盪器。該平台具有機械和運算領域低功耗(< 10 Watt)、重量輕(<1 kg)的特點,非常適合各種人工智慧或者仿生學的實驗。
在清華大學校內的火種計劃的支持下, 本人的研究小組也開始發展多機械自由度魚機器人,目的在發展低功耗,模組化並運用藏本(Kuramoto)神經網路模型的游泳型機器人,主要的研究發表在國內研討會自動化科技國際研討會( Automation 2024) 以及 第29屆人工智慧與應用研討會(簡稱TAAI 2024), 衍生的研究包括了多足蟲(myriapod)的步行機器人,發表在 IEEE CBS Nagoya 2024, 以及利用強化學習中的Q學習法(Q learning)的爬行機器人(Q robot), 發表在 TAAI 並Q robot 的研究成果還獲得 TAAI 2024 的 Runner-up paper award。


AI and Education
Artificial Intelligence has enormous potential in its application to education. Our group is developing various robots for education purpose. We are developing Q robot using reinforcement leaning with small computational loading. The Q robot can learn to crawl within less than 1 hour using look up table representation. Also, we are developing internet of things(IoT) robotic fish. The robotic fish can provide the image as it swims in the aquarium to mimic the “total immersion” experience for the user.
人工智慧在教育領域的應用具有巨大的潛力。 我們小組正在開發各種用於教育目的的機器人。 我們正在開發使用強化學習且計算負載較小的 Q 機器人。 Q 機器人可以使用查找表表示在不到 1 小時的時間內學會爬行。此外,我們正在開發物聯網(IoT)機器魚。機器魚可以在水族箱中游泳時提供圖像,以提供使用者 「完全沉浸」(total immersion) 的體驗 。

